Detroit House, 112 Motor City Dubai , UAE.
Cable Glands for Armoured Cables:
Unarmoured Cable Glands
Cable Glands for Armoured Cables: Ensuring Secure and Reliable Connections
The use of armoured cables is common due to their robustness and ability to withstand harsh environments. Armoured cables are known for their durability and resistance to mechanical damage, making them suitable for demanding applications where protection against external factors is crucial. However, to ensure secure and reliable connections, it is essential to use appropriate cable glands specifically designed for armoured cables. In this article, we’ll explore the importance, types, installation, and key considerations of cable glands for armoured cables.
Importance of Cable Glands for Armoured Cables:
Cable glands play a critical role in securing armoured cables to equipment or enclosures while providing ingress protection against dust, water, and other contaminants. Without proper gland installation, armoured cables are susceptible to damage, leading to electrical faults, safety hazards, and downtime. Therefore, selecting the right cable glands and ensuring their proper installation is essential for maintaining the integrity and performance of electrical installations using armoured cables.

Types of Cable Glands for Armoured Cables:
There are various types of cable glands designed specifically for armoured cables, each offering unique features and benefits. Some common types include:
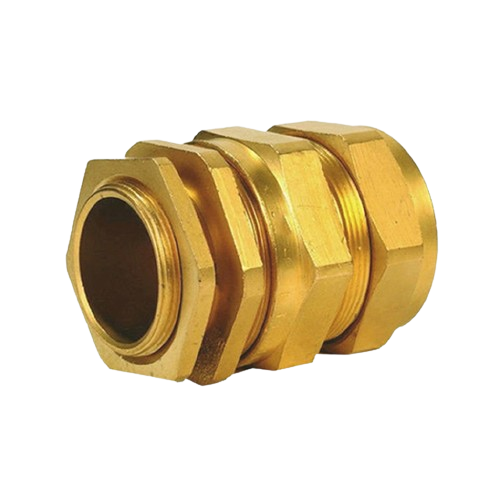
Brass Cable Glands
Brass cable glands are widely used for armoured cables due to their corrosion resistance, durability, and ability to provide a secure connection. They typically feature compression fittings or locking mechanisms that firmly grip the cable’s armour, ensuring a tight seal and effective strain relief.

Stainless Steel Cable Glands:
Stainless steel cable glands are preferred for applications requiring superior corrosion resistance, such as outdoor installations or harsh industrial environments. These glands offer excellent durability and are capable of withstanding extreme temperatures and exposure to corrosive substances.

Nickel-Plated Brass Cable Glands:
Nickel-plated brass cable glands combine the corrosion resistance of brass with the added protection of nickel plating. These glands provide enhanced durability and protection against environmental factors, making them suitable for demanding applications where reliability is paramount.

Installation of Cable Glands for Armoured Cables:
Proper installation of cable glands is crucial to ensuring a secure and reliable connection. The following steps outline the typical installation process:
Prepare the Armoured cable: Strip back the outer sheath of the armoured cable to expose the inner cores. Ensure that the armour layer is undamaged and properly prepared for termination. Insert the cable into the gland. Place the armoured cable through the cable gland, ensuring that the armour is positioned correctly within the gland body.
Secure the Armour: Tighten the gland’s compression mechanism or lock the nut to secure the armour in place. This provides strain relief and prevents the cable from being pulled out of the gland.
Seal the Connection: Apply a sealing compound or gasket to the gland’s entry thread to provide ingress protection against moisture and contaminants.
Secure the Gland: Fix the cable gland to the equipment or enclosure using the appropriate fixing method, such as a locknut or mounting bracket.
Test the Connection: Perform a visual inspection and continuity test to ensure that the cable gland is securely installed and that the connection is electrically sound.
Key Considerations for Selecting Cable Glands:
When choosing cable glands for armoured cables, several factors should be considered to ensure compatibility, reliability, and performance. These include:
Cable Size and Type: Select a cable gland that is compatible with the size and type of armoured cable being used, considering factors such as diameter, construction, and a number of cores.
Environmental Conditions: Assess the environmental conditions, including temperature, moisture levels, and exposure to corrosive substances, to determine the appropriate gland material and ingress protection rating.
Hazardous Area Classification: For installations in hazardous locations, ensure that the cable glands comply with relevant safety standards and certifications for explosive atmospheres.
Installation Method: Choose a cable gland that is suitable for the installation method and equipment enclosure, whether it requires a threaded entry, a compression fitting, or a locking mechanism.
Maintenance Requirements: Consider the ease of maintenance and inspection when selecting cable glands, ensuring that they can be accessed and serviced as needed without disrupting the electrical installation.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, cable glands are essential components of electrical installations using armoured cables, providing secure connections and ingress protection in demanding environments. By selecting the right cable glands and following proper installation procedures, engineers and installers can ensure the reliability, safety, and longevity of electrical systems. With various types and configurations available, it is essential to consider factors such as cable size, environmental conditions, and installation requirements when choosing cable glands for armoured cables and . By prioritizing compatibility, reliability, and performance, engineers can confidently select cable glands that meet the specific needs of their applications, ensuring optimal performance and peace of mind.